With users ranging from enterprise level data centres to single consumers with smart phones requiring higher bandwidth, the demand for newer technologies to deliver these higher data transmission rates is bigger than ever before.
A wide range of technologies exist for the delivery of high throughput, with fibre optic cable considered to be the highest standard. However, fibre optics is not unmatched, especially when all considering economic factors. Millimetre wave wireless technology offers the potential to deliver bandwidth comparable to that of fibre optics but without the logistical and financial drawbacks of the deployments.
Millimetre wave represent the RF Signal spectrum between the frequencies of 30GHz and 300GHz with a wavelength between 1 - 10 millimetres but in terms of wireless networking and communications equipment, the name Millimetre Wave generally corresponds to a few select bands of radio frequencies found around 38, 60 and, more recently, the high potential 70 and 80 GHz bands that have been assigned for the public domain for the purpose of wireless networking and communications.
The image below shows the spectrum from 0 - 100GHz with the most popular Wireless Networking Frequency bands located to represent how much bandwidth is available in the Millimetre Wave regions.
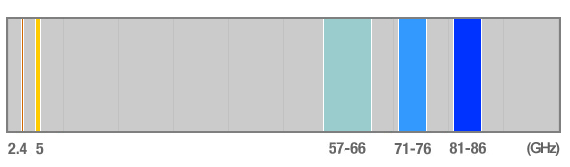
In the UK, there have been 3 frequency bands that have been allocated for commercial Millimetre Wave usage, these are as follows:
57 - 66GHz: The 60GHz Millimetre Wave Band or V-Band is governed by OFCOM for licensed operation. The large amount of signal absorption via atmospheric oxygen and tight regulations make this frequency band more suited to short range, Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint Millimetre Wave solutions. Between 57 - 64GHz the band is licensed and regulated but from 64 - 66GHz the band is unlicensed and self coordinated.
71 - 76GHz and 81 - 86GHz: The 70GHz and 80GHz Millimetre Wave Bands or E-Bands are governed by OFCOM for licensed operation only and are regarded to be the most suited band for Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint, Millimetre Wave Wireless Networking and communication transmission. Each band has a 5GHz spectral range available which totals to be more than all other assigned frequency bands added together. Each 5GHz range can act as a single contiguous wireless transmission channel allowing very efficient use of the whole band and in turn these result in high throughput speeds from 1 to 3 Gbps whilst only using simple modulation techniques such as OOK (On-Off-Keying) or BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying). These throughput speeds are substantially higher than those found in lower frequencies using much more complex and advanced orders of modulation so even higher throughput speeds should be achieved with Millimetre Wave devices when utilising the same advanced techniques. It should be only a matter time before market demand brings these to the forefront.
In the US, another band is available alongside the 3 listed above which is::
92 - 95GHz: The 94GHz Millimetre Wave Band or W-Band is governed by the FCC Part 15 for unlicensed operation also but only for indoor usage. It may also be used to outdoor Point-to-Point applications following the FCC Part 101 regulations but due to a range between 94 - 94.1GHz being excluded, the band is less spectrally efficient than the others.
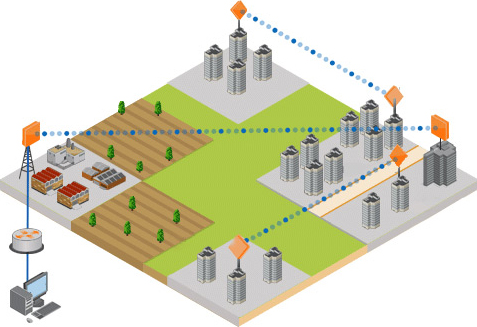
Whilst the number of economic and commerce buildings continues to grow in and around city areas, the requirement for high bandwidth internet is as high as it has ever been. However, many of these buildings rely on old infrastructure transmitting data over out-of-date copper wire due to them not being connected to the main fibre optics grid, strangling the efficiency of business operations.
Despite the majority of these buildings being located within a couple of miles from the fibre optic grid or ring there have previously been no practical and cost effective solutions to install a connection; this is where Millimetre Wave technology can help. By installing a Point-to-Point Millimetre Wave link from a building connected to the fibre optic ring to the target building a high bandwidth, very reliable connection can be made comparable to the actual metro network ring itself.
工业和信息化部日前发布新版《中华人民共和国无线电频率划分规定》,将于7月1日起正式施行。据工业和信息化部相关负责人介绍,新修订的划分规定率先在全球将6GHz频段划分用于5G/6G系统。6GHz频段是中......
现代信息社会中,移动通信是实现信息高效流动的基本手段。近期,第五代移动通信系统(5G)已实现大规模商用。当前,5G长期演进和第六代移动通信系统(6G)成为学术界和产业界的研究热点。实现高通量无线通信的......
毫米波(名词解释⏬)与太赫兹波(名词解释⏬)探测技术在通信、安全、生物检测、频谱分析等领域有着广泛的应用。它们是将承载着毫米波与太赫兹波的光信息转变为电信号的核心技术。高灵敏度、宽波段、快速响应及面阵......
近日,由中国科学院沈阳自动化研究所团队与以色列魏茨曼科学院(WeizmannInstituteofScience)研究团队,联合提出了针对多输入多输出(Multiple-InputMultiple-O......
在时间某处,也许就是此刻新一代的技术变革正激发全新理念的诞生作为未来科技的推动者我们帮助从事前沿研究的高校、公司、研究机构,开启测量新视野使其产品从概念到商用,速度更快科技的迅猛发展带来了很多新的变化......
今日推荐文章作者为东南大学毫米波国家重点实验室主任、IEEEFellow著名毫米波专家洪伟教授,本文选自《毫米波与太赫兹技术》,发表于《中国科学:信息科学》2016年第46卷第8期——《信息科学与技术......
对于投资者来说,军民融合一直是双创中一个重要的领域,由高校实验室走出的项目往往具有高精尖等特点。但是另一方面,这些项目往往都是军转民,而且项目长期处于高校之中难以发现。为了提高科技成果转化,支撑产业发......
由北京航空航天大学承担的“新能源汽车”重点专项“电动汽车智能辅助驾驶关键技术研究与产品开发”项目“智能辅助驾驶环境感知关键技术研究与产品开发”课题研究取得阶段性成果。课题重点围绕77GHz毫米波雷达关......
分析测试百科网讯2017年2月23日,国家重大科学仪器设备开发专项“毫米波成像探测仪研制及产业化示范”项目(2012YQ140037)初步验收会在同方威视密云基地召开。国家科技部资源配置司副司长吴学梯......
意大利电信近日宣布成立一个毫米波(mmWave)频段实验室,用于研究毫米波在5G网络中的应用。意大利电信是欧洲第一家开设毫米波实验室的电信运营商。这个位于都灵的实验室包括远场紧凑天线测试系统和球面近场......